The automotive industry, often associated with innovation and safety, is marked by one of the major problems in its history: Takata’s defective airbags.
This device, designed to protect, has become a risk for millions of motorists.
In 2025, the problem persists, highlighting the need for action.
The Problem
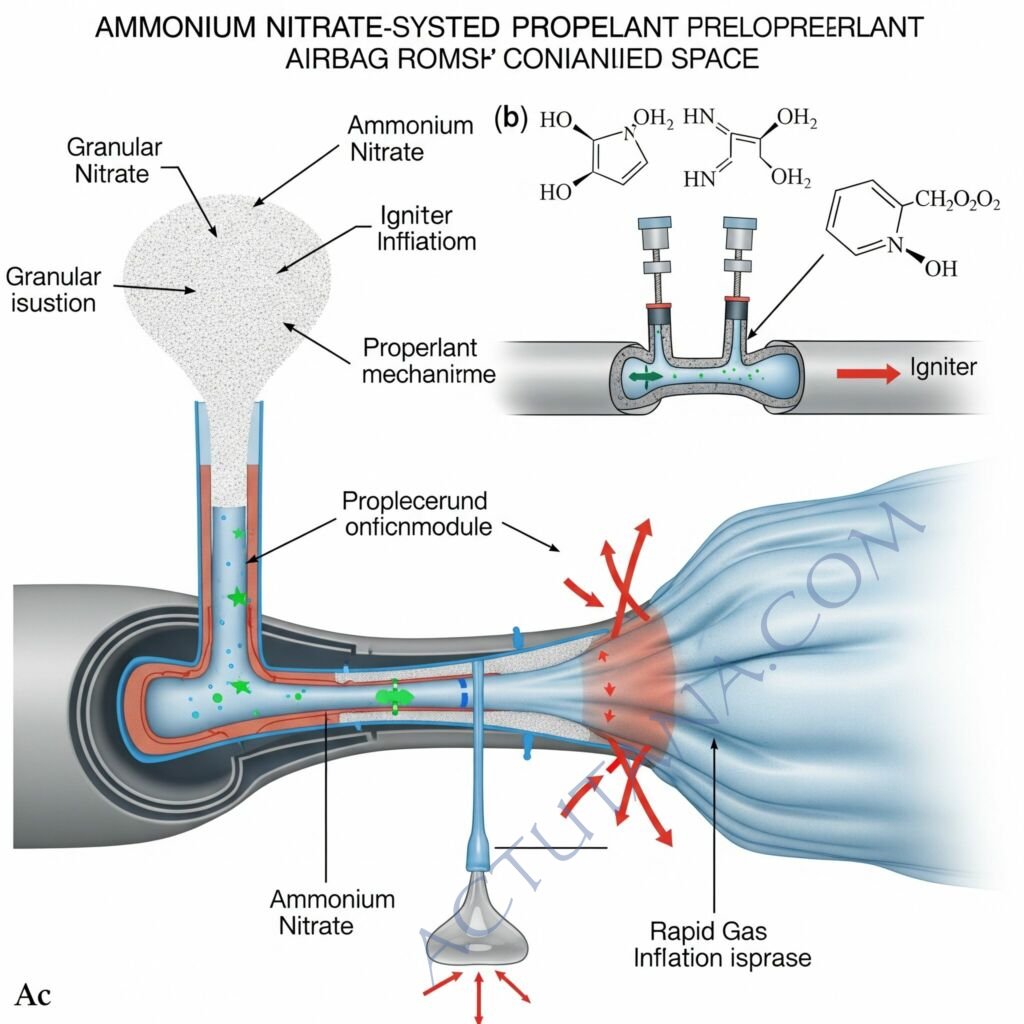
The heart of this problem is the ammonium nitrate-based propellant, used to inflate the airbags in the event of an impact.
This chemical, exposed to heat and humidity over a long period of time, can become unstable.
Instead of a controlled deployment, the airbag explodes with excessive force, propelling metal fragments into the passenger compartment.
This results in serious, sometimes fatal, injuries to the occupants.
Which vehicles are affected?
Tens of millions of vehicles, spanning numerous makes and models produced from the late 1990s to the late 2010s, are affected by this recall.
In France, millions of defective airbags are still in circulation, and deaths related to this defect continue to occur.
Recently, in June 2025, new measures and “stop drive” injunctions were issued for certain models, including the Citroën C3 and DS3, indicating that the situation remains serious.
The Takata problem isn’t just a technical failure; it’s a system failure.
It reveals production decisions focused on cost-cutting at the expense of safety, and a lack of responsiveness that has had human consequences.
The Japanese manufacturer filed for bankruptcy in 2017, but the effects of its actions are still being felt.
What should you do about this risk?
The answer is clear and urgent: act. If you own a potentially affected vehicle, it is important to immediately check whether your car is among the recalled models.
Most manufacturers and transport authorities offer online verification tools, often based on the vehicle identification number (VIN). This check is free and quick.
If your vehicle is affected, make an appointment with your dealer immediately.
Replacement of defective airbags is fully covered by the manufacturer.
Ignoring this warning puts you and your loved ones at risk.
The Takata problem is a lesson for the automotive industry, a reminder of manufacturers’ responsibility to their customers.
What have been the accidents so far?
It is difficult to obtain a comprehensive and accurate list of all recorded accidents involving Takata airbags worldwide. This information is often fragmented and continually updated by authorities and manufacturers.
However, the available data can be summarized.
Worldwide:
- More than 20 deaths have been directly linked to the explosion of Takata airbags.
- Hundreds of injuries, some seriously, have been reported.
- The problem affects tens of millions of vehicles worldwide, across many makes and models produced between 1998 and 2019.
In France (information current as of June 2025):
- The total number of deaths related to Takata airbags in France stands at 18, including 16 overseas and 2 in mainland France.
- At least 25 injuries have been reported.
- A new death was recorded in Guadeloupe in March 2025, and another in Reims in June 2025.
- Currently, 2.5 million vehicles are affected by recalls in France, including 1.7 million with a “stop drive” order (requirement to immobilize the vehicle).
- In June 2025, the Ministry of Transport imposed the immediate immobilization of 600,000 unrepaired Citroën C3s and DS3s produced between 2009 and 2019. An extension of this measure affected an additional 800,000 vehicles, bringing the total to 1.7 million under the “stop drive” injunction.
- As of December 2024, it was estimated that approximately 30% of recalled C3/DS3s had not yet been repaired.
It is important to note that:
- The risk is particularly high in hot and humid regions, such as the overseas departments, as the degradation of ammonium nitrate is accelerated by these conditions.
- The danger increases over time, as component aging and exposure to the elements aggravate the situation.
- Typical injuries are deep lacerations, head trauma, and cervical injuries caused by flying metal fragments.
To find out if your vehicle is affected, It is imperative to check your vehicle identification number (VIN) on the official websites of the manufacturers or the competent authorities.

 5119.73 ar
5119.73 ar 4374.44 ar
4374.44 ar